
حكماء- Admin
- عدد المساهمات : 2700
تاريخ التسجيل : 30/12/2013
 من طرف حكماء الثلاثاء 27 أكتوبر 2015 - 5:52
من طرف حكماء الثلاثاء 27 أكتوبر 2015 - 5:52
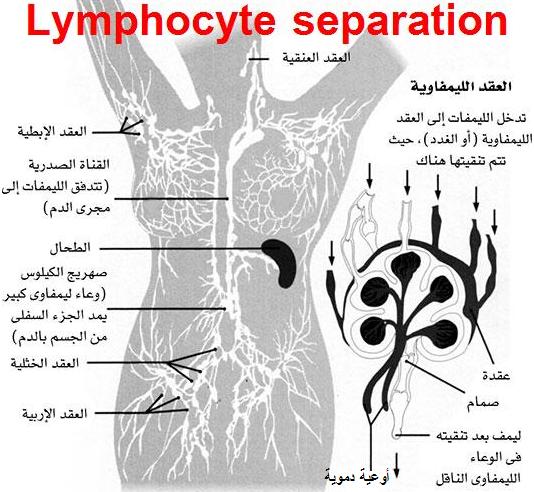
Principle:
Heparinized blood is layered on Ficoll hypaque solution ,then centrifuge for 30 min. at 1600 r.p.m . Whole blood is formed of plasma in which there are cells: lymphocytes, granulocytes, red blood cells and platelets. Ficoll solution has a density gradient greater than that of lymphocytes but less than that of red cells and granulocytes. After centrifugation the red cells and polymorphs pass down to form a pellet at the bottom of the tube, while lymphocytes settle between Ficoll and plasma. A pasteurpipette is used to transfer the lymphocytes to a sterile tube. The lymphocytes are then washed.Cooling centrifuge is used to keep the lymphocyte viability.
Uses of the collected lymphocytes:
1- Assessment of lymphocyte number, using flowcytometry “lymphocytes are labeled with fluorescein labeled anti CD20 for B cells and CD3 for T cells”.
2- Assessment of lymphocyte function.
3- Typing of HLA before organ transplantation.
4- DNA and RNA extraction.
Indirect immunofluorescence technique (I.I.F)
Principle:
Serum auto antibodies bind to the corresponding antigens present in the tissue used on the slide. The Ag-Ab complexes formed are made visible with an antihuman immunoglobulin labeled with fluorescein dye and are visualized with fluorescent microscope.
Clinical application of I.I.F. technique :
1- Detection of auto antibodies in serum e.g ANA.
2- Detection of immune complexes.
Antinuclear antibodies(ANA) by I.I.F technique:
Tissue used:
Hep-2
Principle:
Serum ANA binds to the corresponding Ags present in Hep-2 ,Ag -Ab complexes are made visible with antihuman Ig labeled with fluorescein dye, and are visualized by fluorescent microscope.
Result:
Positive or negative.
Pattern of positive result and interpretation:
1-Homogeneous pattern:
-Diffuse fluorescence of the nucleus.
-Abs against histone.
-Occurs in patients with:
Systemic lupus erythmatosis (SLE).
Drug induced SLE.
2-Peripheral pattern:
-Stronger fluorescence at the outer rim of the nucleus.
-Abs against ds-DNA.
-It is characteristic of active SLE.
3-Speckled pattern:
-The nucleus has grainy appearance.
-Abs against extractable nuclear antigen (Smith antigen and ribonucleoprotein antigen).
-Occurs in patients with:
Scleroderma.
Sjogren’s syndrome.
Mixed connective tissue disease.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
4-Nucleolar pattern:
-Homogeneous staining of the nucleolus.
-Abs against nucleolar Ags.
-Occurs in patients with:
Scleroderma.
Dermatomyositis and poly myositis.
Sjogren’s syndrome.
Less common in SLE and RA.
Interpretation of negative result:
Absence of ANA is strong evidence against the diagnosis of SLE ,because it is highly sensitive screening test.
N.B. SLE with negative ANA occurs some times in patients under treatment.
Anti ds-DNA by I.I.F technique :
Tissue used:
Hemoflagellate called Crithidia Lucidiae.
Principle:
The organism has a giant mitochondrion containing a highly condensed mass of ds-DNA, wich is known as the kinetoplast. It serves as sensitive and specific Ag for detecting Ab against ds-DNA in the serum, Ag Ab complexes are made visible with antihuman Ig labeled with fluorescein dye and are visualized by fluorescent microscope.
Result:
Positive or negative.
Interpretation of positive result:
1-It is highly specific and diagnostic for SLE.
2-Indicates activity of the disease.
3-Indicates renal involvement.
4-Monitor the response to therapy.


 Lymphocyte separation
Lymphocyte separation

 Lymphocyte separation
Lymphocyte separation